Posttraumatic Stress Disorder

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a serious mental health condition that can occur after witnessing or experiencing terrifying events. Individuals with PTSD often experience symptoms such as uncontrollable thoughts, severe anxiety, and flashbacks related to the traumatic event. Many people who have endured trauma may struggle to adjust and cope with daily situations. However, with proper care and support from loved ones, they can usually recover. If the symptoms persist for months or even years and interfere with daily activities, it may be classified as PTSD.
Understanding PTSD:
The severe effects of PTSD can negatively impact many areas of life, including health, enjoyment, relationships, and everyday activities. This condition can affect anyone exposed to traumatic events, such as survivors of accidents, witnesses to violence, and victims of sexual or physical assault.
Symptoms of PTSD:
PTSD symptoms can be categorized into four types:
- Changes in Emotional and Physical Reactions: This may include heightened startle responses or difficulty sleeping.
- Negative Changes in Mood and Thinking: Individuals may experience feelings of hopelessness or difficulty concentrating.
- Avoidance: Avoiding reminders of the trauma, including places, people, or activities.
- Intrusive Memories: This includes flashbacks or distressing memories of the traumatic event.
It is important to note that symptoms can vary from person to person.
How a Therapist Can Help:
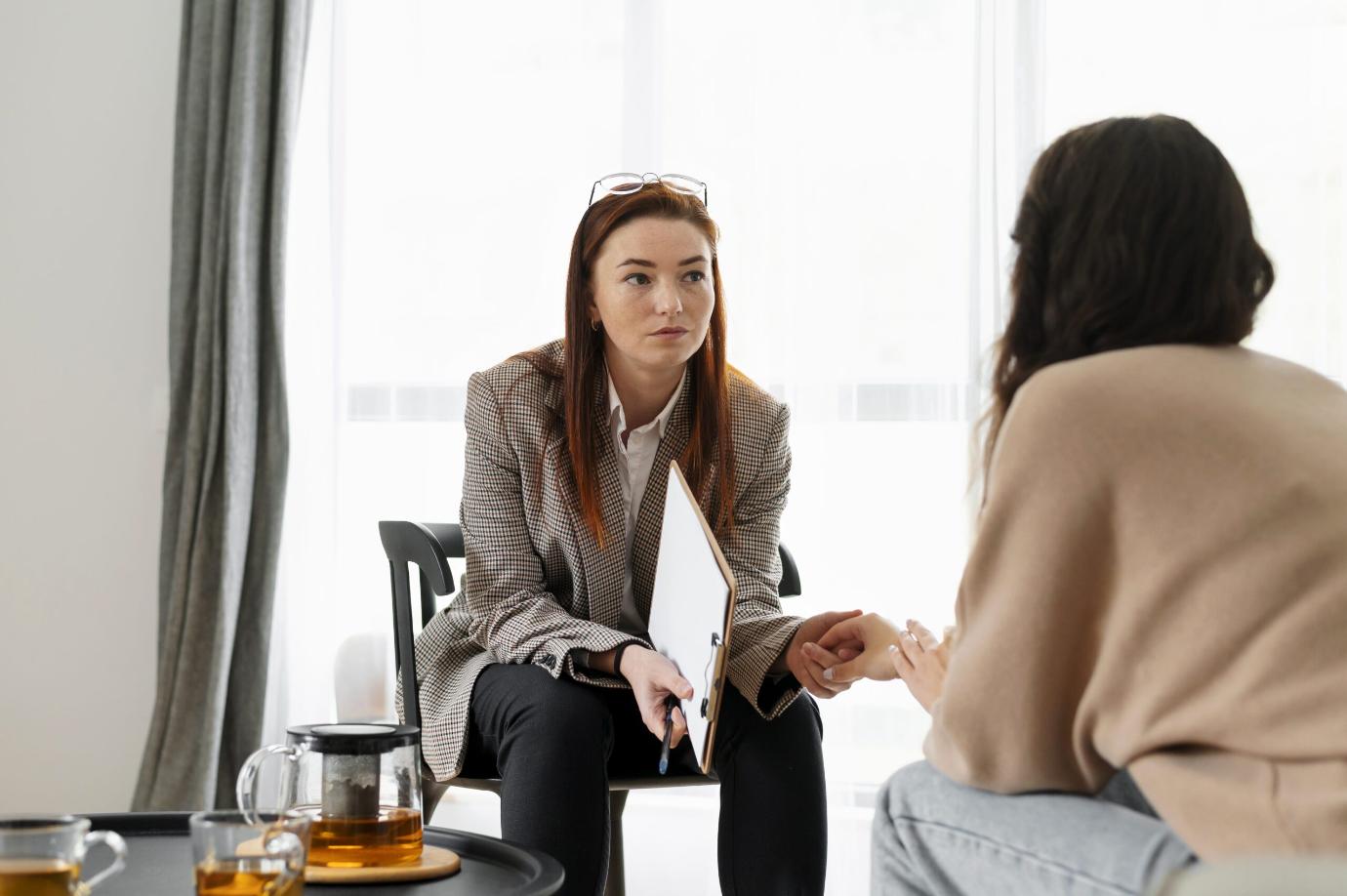
Therapy is highly effective in treating individuals with PTSD. Therapists provide education, support, and therapeutic strategies to help you understand and manage your symptoms. Here are several ways a therapist can assist you:
- Trauma-Focused Psychotherapies:
Trauma-focused psychotherapy is considered the most effective treatment for PTSD. It prioritizes processing the memory of the traumatic events and their meanings. Examples of these therapies include Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), Accelerated Resolution Therapy (ART), Prolonged Exposure (PE) therapy, and Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT).
- Providing a Safe Space:
Therapists create confidential and safe environments where you can openly discuss your trauma and its impact on your life. This supportive setting plays a vital role in the healing process.
- Teaching Coping Strategies:
Therapists introduce healthy coping strategies to help you manage emotional pain. These techniques may include improving sleep patterns, relaxation strategies, and mindfulness practices.
- Addressing Avoidance Behaviors:
Therapy can help you confront avoidance behaviors in a controlled and therapeutic manner. Addressing avoidance is crucial, as it is a key feature of PTSD.
- Improving Self-Esteem:
PTSD can negatively impact self-worth. Therapy can help improve self-esteem through cognitive restructuring and various exercises aimed at challenging negative thoughts.
- Supporting Through Comorbid Conditions:
It is common for individuals with PTSD to also experience other mental health issues, such as substance use, anxiety, or depression. A therapist can identify these issues and provide a holistic approach to treatment.
- Encouraging Social Support:
Therapists may encourage you to seek support from friends and family. They might also recommend group therapy, which allows you to connect with others who have experienced similar traumas.
One of the most important steps in reclaiming your life from the effects of trauma is seeking therapy for PTSD. While it requires courage and dedication, this process can lead to recovery, resilience, and healing. Remember, moving forward means learning to live with your memories in a way that allows you to look ahead while still acknowledging the past.

For Patients
All forms are HIPAA secure
Meet Our Qualified Team